This webpage was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at the University of Wisconsin - Madison.
Gene Ontology
The Gene Ontology project (1) is a major bioinformatics initiative, with the goal to unify the representation of gene and gene product attributes across all species using the AmiGO browser and search engine. Gene ontology covers three domains: cellular components, molecular function, and biological processes.
AmiGO
The following ontologies were found when searching for CFTR in Homo sapiens in AmiGO.
Biomolecular Processes
1. Cholesterol biosynthetic process
2. Cholesterol transport
3. Ion transport
4. Lung development
5. Respiratory gaseous exchange
6. Response to drug
7. Response to estrogen stimulus
8. Response to peptide hormone stimulus
9. Transepithelial chloride transport
10. Transmembrane transport
11. Transport
12. Vasodilation
Cellular Components
1. Apical plasma membrane
2. Basolateral plasma membrane
3. Chloride channel complex
4. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
5. Early endosome
6. Endoplasmic reticulum sec complex
7. Integral to membrane
8. Membrane
Molecular Functions
1. ATP binding
2. ATP-binding and phosphorylation-dependent chloride channel activity
3. ATPase activity
4. Channel-conductance controlling ATPase activity
5. Chloride channel activity
6. Enzyme binding
7. Hydrolase activity
8. Ion channel activity
9. Nucleotide binding
10. PDZ domain binding
Biomolecular Processes
1. Cholesterol biosynthetic process
2. Cholesterol transport
3. Ion transport
4. Lung development
5. Respiratory gaseous exchange
6. Response to drug
7. Response to estrogen stimulus
8. Response to peptide hormone stimulus
9. Transepithelial chloride transport
10. Transmembrane transport
11. Transport
12. Vasodilation
Cellular Components
1. Apical plasma membrane
2. Basolateral plasma membrane
3. Chloride channel complex
4. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
5. Early endosome
6. Endoplasmic reticulum sec complex
7. Integral to membrane
8. Membrane
Molecular Functions
1. ATP binding
2. ATP-binding and phosphorylation-dependent chloride channel activity
3. ATPase activity
4. Channel-conductance controlling ATPase activity
5. Chloride channel activity
6. Enzyme binding
7. Hydrolase activity
8. Ion channel activity
9. Nucleotide binding
10. PDZ domain binding
GOA
Gene Ontology Annotation Project (2) aims to provide high-quality gene ontology annotations to proteins in the UniProt Knowledgebase (UniProtKB) and International Protein Index (IPI).
The CFTR protein alone does not have a GO id, because it is not classified under any of the three ontologies. The only CFTR complex with a GO annotation is the CFTR-NHERF-ezrin complex.
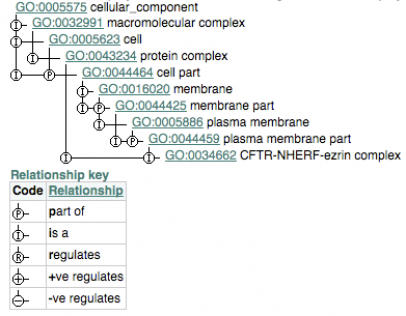
CFTR-NHERF-ezrin complex GO id: GO:0034662
This protein complex contains ezrin, Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor (NHERF, also called EBP50), and two copies of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). The CFTR molecules interact with NHERF via their cytoplasmic tail domains. The complex is thought to link the CFTR channel to the actin cytoskeleton and contribute to the regulation of channel activity.
The CFTR protein alone does not have a GO id, because it is not classified under any of the three ontologies. The only CFTR complex with a GO annotation is the CFTR-NHERF-ezrin complex.
CFTR-NHERF-ezrin complex GO id: GO:0034662
This protein complex contains ezrin, Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor (NHERF, also called EBP50), and two copies of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). The CFTR molecules interact with NHERF via their cytoplasmic tail domains. The complex is thought to link the CFTR channel to the actin cytoskeleton and contribute to the regulation of channel activity.
Ancestor Chart
Below is an alternative way to display of a section of gene ontology, called an ancestor chart. It provides a concise view of the relationships that connect gene ontology terms.
Analysis
Nearly all of the GO terms assembled by AmiGO were unsurprising as they related to membrane bound ion transport, ATP binding, and chloride channels. This is logical because CFTR is an ATP-reducing chloride channel complex.
The only unexpected GO term findings are "cholesterol transport", "cholesterol biosynthetic process" and "response to estrogen stimulus".
The only unexpected GO term findings are "cholesterol transport", "cholesterol biosynthetic process" and "response to estrogen stimulus".
_______________
References
1. GO Consortium. March 18, 2010. http://www.geneontology.org
2. Gene Ontology Annotation. March 18, 2010. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/GOA/
References
1. GO Consortium. March 18, 2010. http://www.geneontology.org
2. Gene Ontology Annotation. March 18, 2010. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/GOA/
Alexandra Reynolds
[email protected]